Apr 16, 2024
Introduction
In the realm of real estate, aesthetics and presentation play a pivotal role, especially within architecture. How a structure looks, flows, and functions holds immense significance. Hence, any technology that enhances stakeholders' view and appreciation of a structure is invaluable.
While virtual reality (VR) and rendering have been popular visualization tools, augmented reality (AR) is emerging as a transformative technology for the industry. Valued at $57.26 billion in 2023 with a compound annual growth rate of 39.8% projected until 2030, AR is set to revolutionize the architectural landscape.
Augmented Reality: Redefining Architecture Visualization
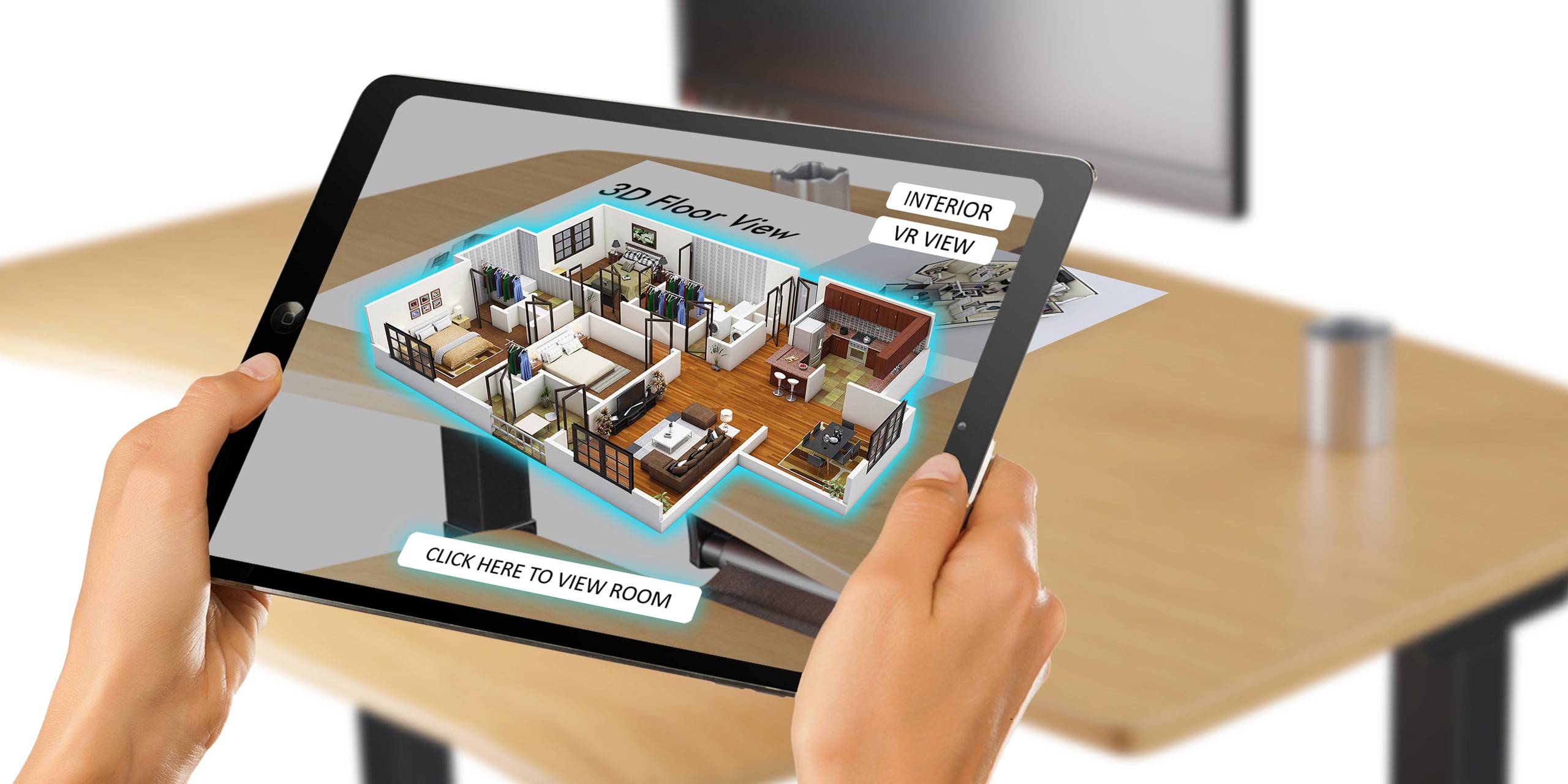
Augmented reality, a component of extended reality (XR), overlays computer-generated elements onto a person's perception of the physical world, creating an interactive and engaging hybrid environment. This technology offers immense value in attracting clients, managing expectations, and closely coordinating real estate development projects.
Applications of AR in Architecture
While AR gained initial popularity through consumer applications like Pokémon GO, its potential in business, particularly architecture, is vast. In architecture, AR is integrated with virtual 3D models, often embedded with Building Information Modeling (BIM), to provide accurate representations of design concepts.
Architects and design professionals can leverage AR to walk around enhanced spaces, gaining valuable insights into design elements, installations, and potential errors before construction begins. Additionally, AR seamlessly integrates with other technologies like VR for real-time data visualization and modification, enhancing efficiency in architectural processes.
Benefits of Augmented Reality in Architecture
AR offers several benefits in architecture and construction:
Accurate Timelines: AR bridges the gap between design and construction by providing real-time access to critical information, improving task management and decision-making, and ensuring project timelines are met.
Facilitated Collaboration: AR enables stakeholders from different disciplines to collaborate remotely, view proposed models, and share constructive ideas with precision, ensuring functional and structurally sound designs.
Resource Optimization: AR minimizes health and safety risks, enhances ground crew efficiency, and optimizes resource utilization through features like digital twins and improved logistics management.
Enhanced Client Understanding: AR creates immersive environments within the real world, helping clients visualize structures, interact with models, and make informed decisions, improving overall project understanding and satisfaction.
Safety Hazard Assessment: Virtual simulations in AR can assess potential safety hazards on construction sites, providing real-time safety information to workers and reducing the risk of accidents.
Early Issue Identification: AR allows architects to examine proposed designs comprehensively, identifying and rectifying design inconsistencies early in the process, ultimately reducing rework and project costs.
Conclusion
Augmented reality is reshaping the architectural landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for design visualization, collaboration, and client engagement. As the industry embraces AR, architecture professionals must familiarize themselves with its applications and benefits to remain competitive and deliver exceptional experiences to clients.